Quality Text, Robust Vision: The Role of Language in Enhancing Visual Robustness of Vision-Language Models
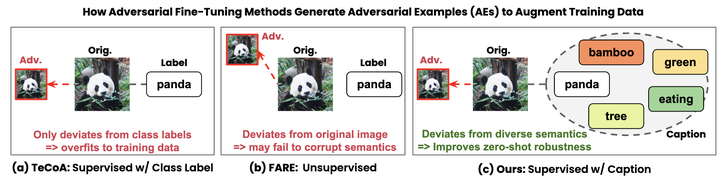 Image credit: Unsplash
Image credit: UnsplashAbstract
Defending pre-trained vision-language models (VLMs), such as CLIP, against adversarial attacks is crucial, as these models are widely used in diverse zero-shot tasks, including image classification. However, existing adversarial training (AT) methods for robust fine-tuning largely overlook the role of language in enhancing visual robustness. Specifically, (1) supervised AT methods rely on short texts (e.g., class labels) to generate adversarial perturbations, leading to overfitting to object classes in the training data, and (2) unsupervised AT avoids this overfitting but remains suboptimal against practical text-guided adversarial attacks due to its lack of semantic guidance. To address these limitations, we propose Quality Text-guided Adversarial Fine-Tuning (QT-AFT), which leverages high-quality captions during training to guide adversarial examples away from diverse semantics present in images. This enables the visual encoder to robustly recognize a broader range of image features even under adversarial noise, thereby enhancing robustness across diverse downstream tasks. QT-AFT overcomes the key weaknesses of prior methods – overfitting in supervised AT and lack of semantic awareness in unsupervised AT – achieving state-of-the-art zero-shot adversarial robustness and clean accuracy, evaluated across 16 zero-shot datasets. Furthermore, our comprehensive study uncovers several key insights into the role of language in enhancing vision robustness; for example, describing object properties in addition to object names further enhances zero-shot robustness. Our findings point to an urgent direction for future work – centering high-quality linguistic supervision in robust visual representation learning.